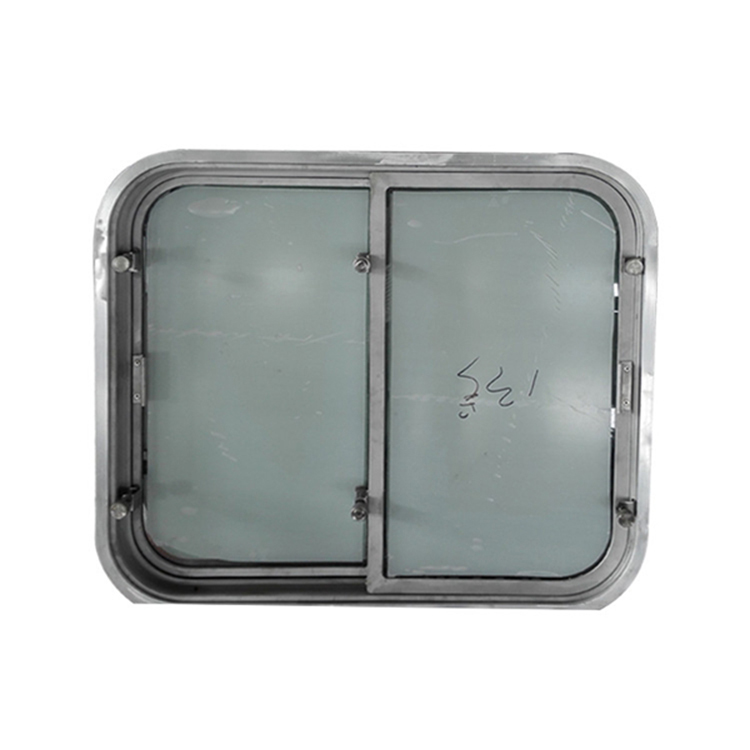
Ship windows are an essential component of a vessel’s structure, providing natural light and ventilation to the interior spaces while also protecting them from the elements. As such, it is crucial that ship windows are tested for safety and performance to ensure they meet the necessary standards and regulations.
There are several key methods by which ship windows are tested for safety and performance:
Structural Testing: One of the primary considerations for ship windows is their ability to withstand the forces exerted on them by the environment, such as wind, waves, and impacts. Structural testing involves subjecting the window to various tests, including pressure tests, impact tests, and fatigue tests, to assess its strength and stability under different conditions.
Water Resistance Testing: Ship windows must also be tested for their ability to prevent water ingress into the interior spaces of the vessel. Water resistance testing involves exposing the window to water under controlled conditions to evaluate its sealing capabilities and determine whether any leakage occurs.
Thermal Performance Testing: Ship windows are also tested for their thermal performance, including their ability to retain heat and reduce energy loss. Thermal performance testing involves measuring the window’s thermal transmittance (U-value) and solar heat gain coefficient to determine its energy efficiency.
Fire Safety Testing: Ship windows must meet specific fire safety requirements to ensure the safety of passengers and crew in the event of a fire onboard. Fire safety testing involves subjecting the window to high temperatures to assess its fire resistance and smoke control capabilities.